Deliverables and milestones are the key elements of a Horizon Europe proposal work plan. They are part of the Work Breakdown Structure (in Work Packages (WPs) and tasks) and will be scrutinised by the evaluators in the Implementation Section to assess the credibility of your proposal. When your proposal is accepted, both deliverables and milestones become important tools for project management, as they will be used by all stakeholders (consortium members and the European Commission) to assess the progress of different project tasks.
Difference between deliverables and milestones in Horizon Europe
As stated in the template for proposals, a deliverable is "a report that is sent to the Commission or Agency providing information to ensure effective monitoring of the project. There are different types of deliverables (e.g. a report on specific activities or results, data management plans, ethics or security requirements)", but even if your deliverable is a Demonstrator or a Prototype, you will be asked to submit a written report detailing the characteristics of the demonstrator/prototype and the process to build it.
On the other hand, according to the the template for proposals, milestones are "control points in the project that help to chart progress. Milestones may correspond to the achievement of a key result, allowing the next phase of the work to begin. They may also be needed at intermediary points so that, if problems have arisen, corrective measures can be taken. A milestone may be a critical decision point in the project where, for example, the consortium must decide which of several technologies to adopt for further development. The achievement of a milestone should be verifiable".
When do you need a deliverable?
Deliverables must be defined with care and you must provide a sufficient number of them in order to reassure evaluators on the seriousness of the project. It is generally considered good practice to have at least one deliverable per task (in most cases at the end of the task) to assess the quality of its achievements and justify the funding. For long tasks (more than 18 months), an intermediary deliverable can be useful.
Deliverables can be classified in three different categories:
- Deliverables are often used as a mean of reporting, where project members provide more details about the implementation of a specific task than in the interim and final reports.
- However, winning proposals often include more interesting deliverables that we will call “key deliverables”. These key deliverables do not merely report on progress but are also considered concrete results of the project. This is the case of prototypes or policy reports for example.
- Finally, some deliverables are produced to help the project develop, such as specification deliverables or preliminary analysis. In these cases, the deliverable is of peculiar importance because it will influence the rest of the project.
Note also that deliverables are instrumental to keep your consortium involved in the project. Therefore, all partners should be responsible for at least one deliverable and contribute to some others. It is also important to make sure that the workload required by deliverables is balanced and matches the number of person-months allocated to each partner.
Planning deliverables
Discussing and writing deliverables will be the essence of many projects, with a high risk to be overwhelmed. To prevent this, you should try to schedule the project deliverables evenly all along the project (for example one or two per month). It is also advised not to schedule deliverables during the two-month period allocated to interim and final reporting. Even better, try not to plan deliverables in the two months before the end of a reporting period. In this case, should one of the deliverables be late, you will have some time to remedy the problem before your interim/final report is sent (or before a review).
Note: The same apply for a summer break (nobody likes to write deliverables in August).
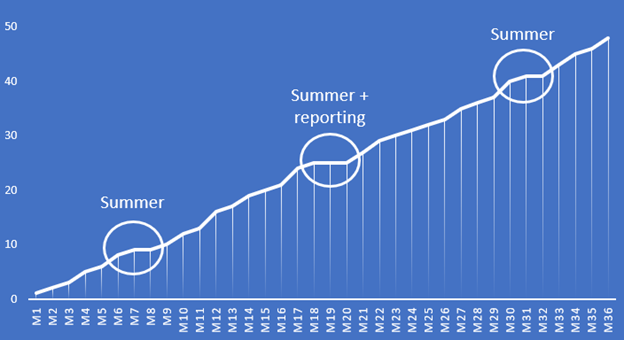
Figure 1: This graph shows the cumulative number of deliverables over a 36-month project (starting on the 1st of January). The deliverable plan leaves some breaks during summer and reporting periods.